• Symptoms: fatigue (anaemia), infections (neutropenia), bleeding (thrombocytopenia)
• Diagnosis: >20% blasts in bone marrow
• Auer rods, MPO-positive
• Adults; rapid progression
• Risk factors: benzene, chemotherapy, MDS
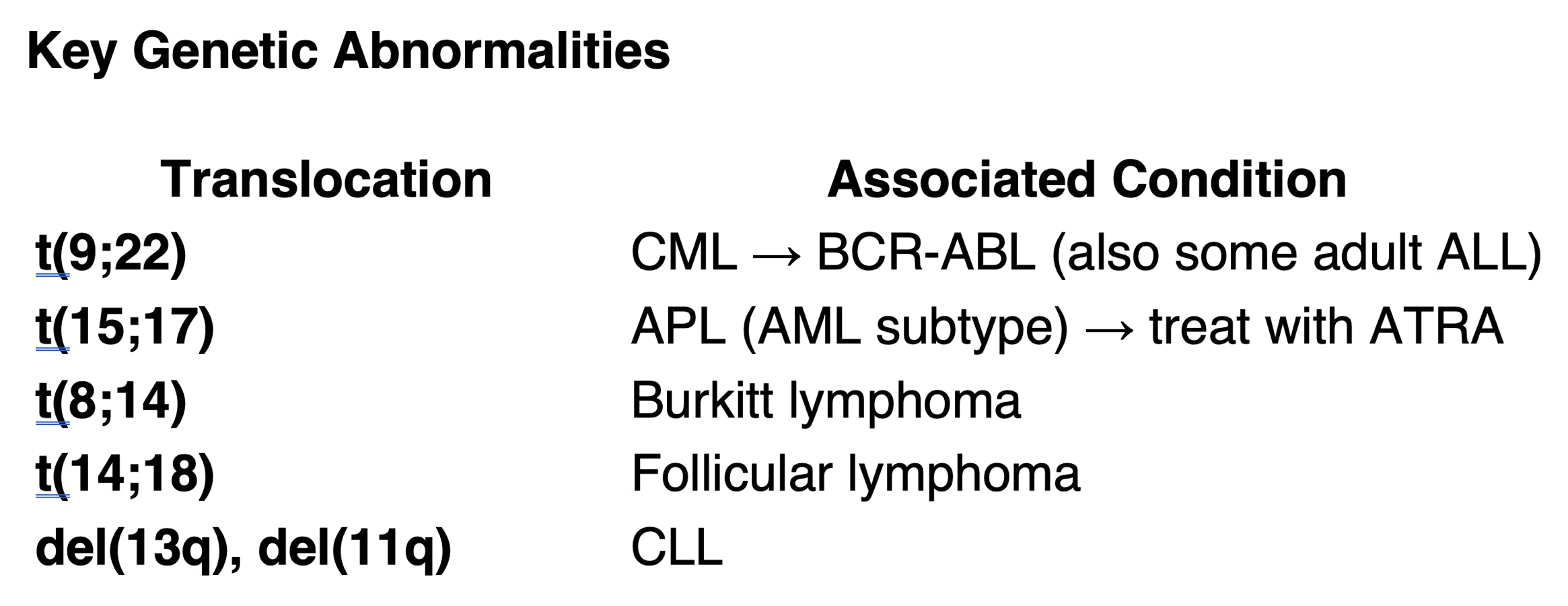
• Special subtype: APL (M3) — t(15;17), treat with ATRA
• Children; often presents with mediastinal mass, CNS involvement
• Immunophenotype:
o TdT-positive (marker of lymphoid precursors)
o CD10+ (pre-B), CD3+ (T-cell ALL)
• CNS prophylaxis essential (e.g. intrathecal methotrexate)
• t(9;22) → Philadelphia chromosome, BCR-ABL fusion gene
• Features: fatigue, weight loss, massive splenomegaly, ↑ WBC, basophilia
• Triphasic: chronic → accelerated → blast crisis
• Treatment: imatinib (tyrosine kinase inhibitor)
• Elderly, often asymptomatic
• Features:
o Lymphocytosis
o Smudge cells on blood film
o Recurrent infections (hypogammaglobulinaemia)
o Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
• Can transform into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Richter’s transformation)
• Clonal stem cell disorder → ineffective haematopoiesis
• Features:
o Cytopenias
o Dysplastic changes in marrow
• Risk: progression to AML
• Diagnosis: hypercellular marrow with peripheral cytopenias
• Reed–Sternberg cells
• Contiguous spread
• B symptoms: fever, night sweats, weight loss
• Common subtype: nodular sclerosis
• Staging: Ann Arbor (I–IV + A/B symptoms)
• B or T cell origin
• Non-contiguous spread
• Key subtypes:
o Burkitt: t(8;14), c-MYC
o Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): aggressive
o Follicular: t(14;18), indolent
o Marginal zone: often MALT-associated
• Malignant plasma cells → monoclonal protein
• CRAB criteria:
o C: hyperCalcaemia
o R: Renal impairment
o A: Anaemia
o B: Bone pain/lytic lesions
• Investigations:
o Serum electrophoresis: M-protein (IgG or IgA)
o Urine: Bence Jones protein (free light chains)
o Bone marrow: >10% clonal plasma cells
o Rouleaux formation, ↑ β2-microglobulin
• Treatment: bortezomib, lenalidomide, steroids, autologous stem cell transplant
• ↑ Hb/Hct, JAK2 mutation, ↓ EPO
• Risk of thrombosis, bleeding
• Rx: venesection, aspirin
• ↑ Platelets, haemorrhage/thrombosis risk
• JAK2/CALR/MPL mutations
• Rx: hydroxycarbamide if high risk
• Marrow fibrosis → tear-drop RBCs, extramedullary haematopoiesis, splenomegaly
• May transform to AML
• Bone marrow: dry tap
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Author & Educational Disclaimer
Author:
Dr Phillip Cockrell BM FRCP DipClinEd
Dr Phillip Cockrell is a UK Consultant Physician in Internal Medicine, currently working at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth University Hospitals NHS Trust. He has previously worked as a registrar across Intensive Care Medicine, Gastroenterology, Cardiology, Stroke Medicine, Acute Medicine, and Respiratory Medicine.
He has held senior leadership roles including Associate Clinical Director of the Acute Medical Unit, Clinical Director of Internal Medicine, and Chief of Medicine. Dr Cockrell has over 15 years’ experience in postgraduate medical education, having lectured extensively across the MRCP syllabus and contributed to MRCP revision teaching and course development.
Dr Cockrell holds a Bachelor of Medicine (BM), Fellowship of the Royal College of Physicians (FRCP), and a Diploma in Clinical Education (DipClinEd). His teaching approach is based on structured consolidation of complex medical topics to support efficient and effective revision for postgraduate examinations.
Purpose of this content:
The material on this page is intended solely for educational purposes to support revision for the MRCP (UK) Part 1 examination. It reflects examination-relevant principles of internal medicine and is designed to aid learning and pattern recognition.
Medical disclaimer:
This content is designed for postgraduate medical examination revision and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment guidance and must not be used as a substitute for professional clinical judgement, local guidelines, or specialist consultation. Clinical decisions should always be made in the context of individual patient circumstances and current national guidance.