o Stasis: immobility, long-haul travel, surgery
o Endothelial injury: trauma, surgery, central lines
o Hypercoagulability: pregnancy, malignancy, inherited thrombophilia
• Other factors:
o Oestrogen therapy: HRT, combined oral contraceptives
o Obesity, smoking, increasing age
• Factor V Leiden mutation: most common inherited cause; activated protein C resistance
• Prothrombin gene mutation (G20210A): ↑ thrombin production
• Protein C deficiency
• Protein S deficiency
• Antithrombin III deficiency
• Consider testing if:
o Unprovoked VTE <40 years
o Recurrent VTE
o VTE in unusual sites (e.g. cerebral, mesenteric veins)
o Strong family history
• Antiphospholipid syndrome
• Malignancy
• Nephrotic syndrome, myeloproliferative neoplasms
• Features:
o Arterial and venous thrombosis
o Recurrent miscarriages
o Livedo reticularis, thrombocytopenia
• Antibodies:
o Lupus anticoagulant (prolongs APTT but is prothrombotic)
o Anti-cardiolipin
o Anti-β2 glycoprotein I
• Diagnosis: clinical + ≥1 antibody positive on 2 occasions 12 weeks apart
• Management:
o Lifelong anticoagulation (warfarin preferred) if thrombosis occurs
o INR target 2.5–3.5 for recurrent events
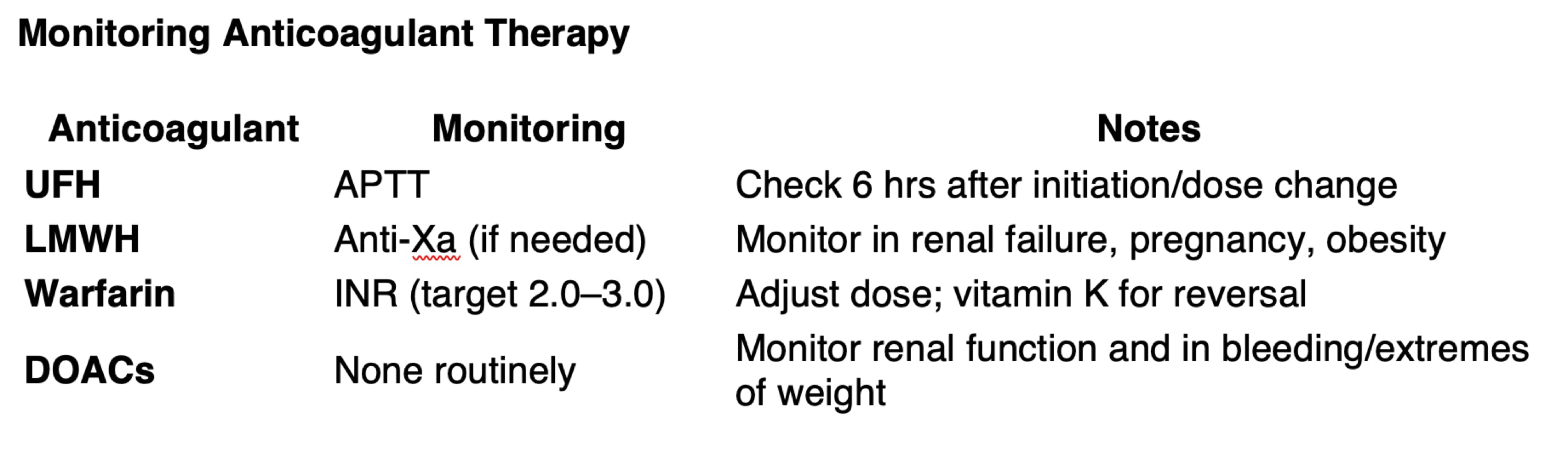
• Unfractionated heparin (UFH):
o IV use, monitor APTT
o Short half-life, reversible with protamine sulfate
• Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH):
o Subcutaneous, predictable dosing
o No routine monitoring, but check anti-Xa levels in renal failure, obesity, pregnancy
• Vitamin K antagonist
• Monitor INR (target 2.0–3.0 in most cases)
• Interacts with many drugs and foods (esp. antibiotics, leafy greens)
• Reversal: vitamin K, prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC)
• Apixaban, rivaroxaban (factor Xa inhibitors)
• Dabigatran (direct thrombin inhibitor)
• No routine monitoring; adjust for renal function
• Reversal:
o Idarucizumab for dabigatran
o Andexanet alfa (factor Xa inhibitor reversal)
• Indications:
o STEMI (if PCI unavailable within 120 mins)
o Massive PE with haemodynamic instability
o Ischaemic stroke: <4.5 hours from onset
• Agents:
o Alteplase (tPA): fibrin-specific
o Streptokinase: antigenic; less commonly used now
• Major bleeding risk, especially intracranial
• Oestrogen-containing therapy (OCP, HRT):
o Increases VTE risk
o Contraindicated in:
Known thrombophilia
History of VTE
Strong family history of VTE
• Progestogen-only contraceptives are safer alternatives
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Author & Educational Disclaimer
Author:
Dr Phillip Cockrell BM FRCP DipClinEd
Dr Phillip Cockrell is a UK Consultant Physician in Internal Medicine, currently working at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth University Hospitals NHS Trust. He has previously worked as a registrar across Intensive Care Medicine, Gastroenterology, Cardiology, Stroke Medicine, Acute Medicine, and Respiratory Medicine.
He has held senior leadership roles including Associate Clinical Director of the Acute Medical Unit, Clinical Director of Internal Medicine, and Chief of Medicine. Dr Cockrell has over 15 years’ experience in postgraduate medical education, having lectured extensively across the MRCP syllabus and contributed to MRCP revision teaching and course development.
Dr Cockrell holds a Bachelor of Medicine (BM), Fellowship of the Royal College of Physicians (FRCP), and a Diploma in Clinical Education (DipClinEd). His teaching approach is based on structured consolidation of complex medical topics to support efficient and effective revision for postgraduate examinations.
Purpose of this content:
The material on this page is intended solely for educational purposes to support revision for the MRCP (UK) Part 1 examination. It reflects examination-relevant principles of internal medicine and is designed to aid learning and pattern recognition.
Medical disclaimer:
This content is designed for postgraduate medical examination revision and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment guidance and must not be used as a substitute for professional clinical judgement, local guidelines, or specialist consultation. Clinical decisions should always be made in the context of individual patient circumstances and current national guidance.